Overview
PECmd is a command line tool developed by Eric Zimmerman, to process Prefetch files (.pf) on Windows operating systems, identifying items such as:
- Volume information
- Files and Directories referenced
- Executions time (up to last 8 for Win8+)
- Total execution count
PECmd can output the parsed prefetch files into .csv, json and HTML formats for further analysis. It should be noted that Windows Servers do not have prefetch enabled by default, information on enabling this service can be found on Darkcybe - Evidence of Execution
Instructions
Parsing a Single Prefetch File
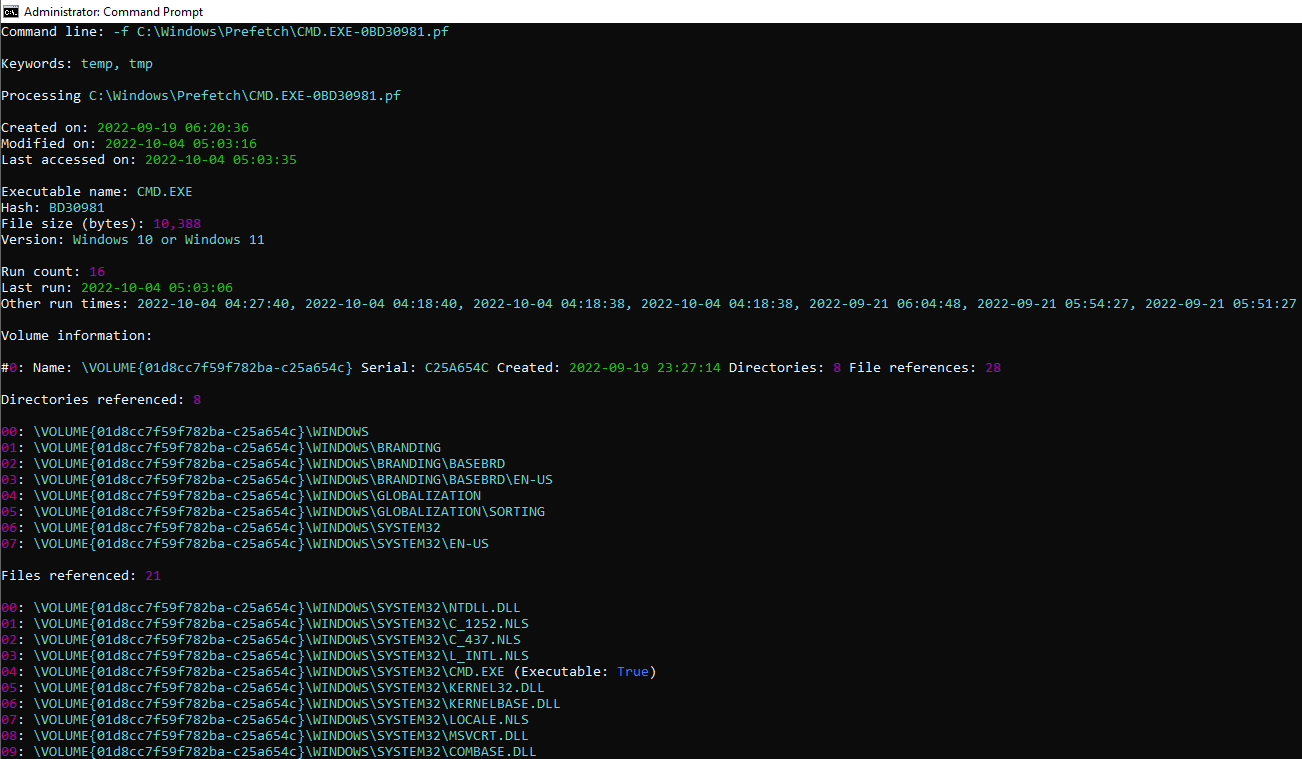
Parses the prefetch file for bad.exe and writes the output to a .csv file for further analysis. A single entry will be returned to STDOUT
1
PECmd.exe -f \PATH\TO\bad.exe-2222BD1A.pf
Output
Parsing all Prefetch Files within a Directory
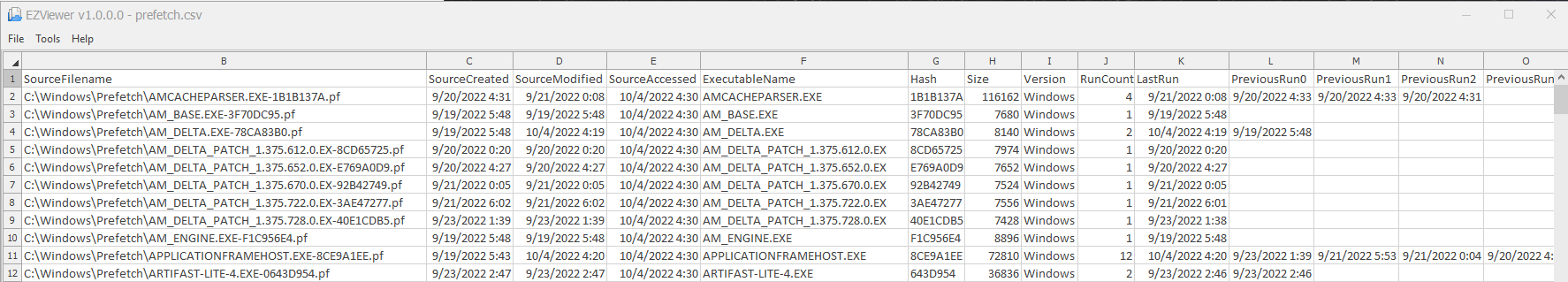
Parses all prefetch files within a supplied directory. The example depicts parsing all .pf files within the default Windows prefetch directory and writes the output to a .csv file for further analysis. The q switch prevents the tool from printing the results to STDOUT. Two files will be output, a standard parsing of the entries Prefetch directory and a second timeline view of individual application executions.
1
PECmd.exe -d “E:\Windows\Prefetch” –csv “G:\Cases\001\Suspect_Machine_1\Prefetch_all.csv -q
- Interesting Fields
- SourceCreated = .pf Creation Timestamp
- SourceModified = .pf Modification Timestamp
- SourceAccessed = .pf Last Access Timestamp (Will be overwritten by tooling)
- ExecutableName = Name of executable
- RunCount = Amount of times executed
- LastRun = Timestamp of last execution
- PreviousRun# = Timestamps of previous executions
Output
Date/Time of Execution Prefetch files are created roughly ~10 seconds after an executable is executed, therefore the modification (last execution) and creation (first execution) DTG’s may be 10 seconds after displayed times on the prefetch listings.
